Filing taxes correctly is a crucial part of personal and business financial management. Understanding tax filing rules explained ensures that individuals, freelancers, and business owners comply with the law, avoid penalties, and maximize their legal tax benefits. Mistakes in filing can result in fines, audits, or missed deductions, which can have long-term financial consequences.
This detailed guide explains the rules, obligations, procedures, and best practices for filing taxes accurately and efficiently.
What Are Tax Filing Rules?

Tax filing rules are the regulations, guidelines, and procedures laid out by government tax authorities to determine who should file taxes, what must be reported, how taxes should be paid, and when returns must be submitted.
These rules differ based on:
- Type of taxpayer (individual, freelancer, small business, corporation)
- Income level and sources of income
- Jurisdiction and applicable tax laws
By following tax filing rules, taxpayers ensure that they pay the correct amount, avoid penalties, and maintain accurate records.
Importance of Understanding Tax Filing Rules
- Avoid Penalties and Fines
Late or incorrect filing may result in fines, interest on unpaid taxes, or legal proceedings. - Ensure Legal Compliance
Complying with tax laws protects you from disputes with tax authorities. - Maximize Deductions and Benefits
Understanding rules helps you claim all eligible deductions, exemptions, and credits to minimize taxable income. - Financial Planning
Accurate tax filing gives a clear picture of your finances, helping with budgeting, investment decisions, and retirement planning. - Reduce Audit Risks
Correct filing with proper documentation lowers the risk of audits or investigations.
Tax Filing Rules Explained Step by Step
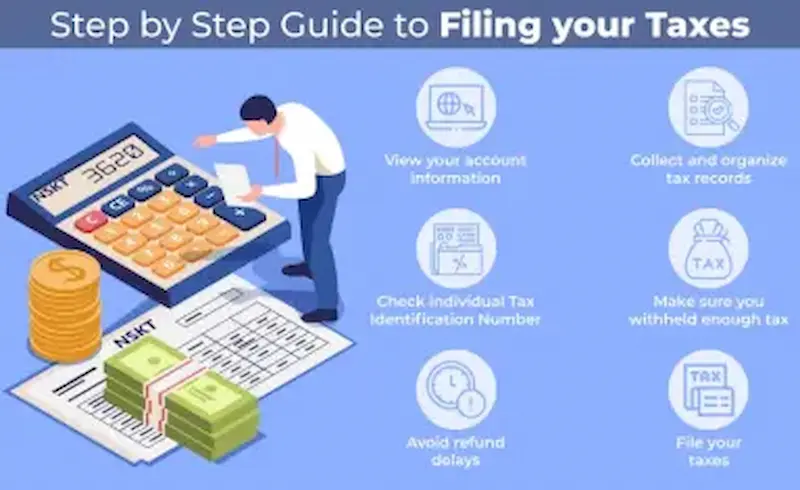
1. Identify Who Must File
- Individuals: Anyone earning above the taxable income threshold must file an annual return. This includes salary, freelance income, rental income, capital gains, or investment income.
- Businesses: Corporations, partnerships, and self-employed individuals must file depending on their income, structure, and type of taxes (income, VAT/GST, payroll taxes).
2. Know Your Filing Deadlines
Deadlines vary by country, type of income, and taxpayer category:
- Individuals: Usually an annual filing period, with possible extensions for online submissions.
- Businesses: Often quarterly or annual filing requirements for corporate taxes, indirect taxes (GST/VAT), and payroll taxes.
Missing deadlines may result in late fees, interest, or penalties.
3. Maintain Accurate Financial Records
Proper record-keeping is crucial for compliance and claiming deductions:
- Salary slips and employment documents
- Bank statements and investment records
- Receipts for deductions such as health insurance or education expenses
- Business invoices, payroll records, and expense proofs
Records should be stored for at least 5–7 years, depending on local regulations.
4. Report All Sources of Income
Tax authorities require disclosure of all income:
- Salary, bonuses, or allowances
- Freelance or self-employment income
- Rental income from property
- Investment income: dividends, interest, capital gains
Undisclosed income can lead to audits and penalties.
5. Claim Eligible Deductions and Exemptions
Deductions reduce taxable income and can significantly lower your tax bill:
- Retirement fund contributions (pension, 401(k), EPF)
- Health insurance premiums for self and dependents
- Education and tuition fees for self or dependents
- Home loan principal and interest payments
- Charitable contributions to registered organizations
Ensure all claims are supported with valid documentation.
6. Calculate Your Tax Liability
Determine your taxable income after deductions and exemptions. Apply the applicable tax slab, rate, or formula based on your jurisdiction. Include any advance tax or self-assessment tax if required.
7. Choose the Correct Filing Method
- Online Filing (E-filing): Fast, convenient, and provides instant acknowledgment.
- Paper Filing: Still accepted in some regions, though slower and more error-prone.
- Professional Filing: Recommended for complex scenarios with multiple income streams, business income, or foreign investments.
8. Double-Check Before Submission
Verify all details carefully:
- Correct PAN/TIN numbers
- Accurate income and deduction entries
- Proper attachments for proofs
- Correct bank account information for refunds
Errors can delay processing or trigger notices from authorities.
You may also like to read this:
Tax Saving Calculator: Estimate Your Tax Savings Easily
Online Financial Tools: Track, Plan, and Manage Money Easily
Budget and Tax Tools: Plan Finances and Taxes Easily
How to File Taxes Correctly: Step-by-Step Guide
Income Tax Compliance Guide: Rules & Tips for Individuals
9. Submit Your Tax Return
After verifying all details, submit the return via the chosen method. Retain acknowledgment receipts or confirmation numbers for future reference.
10. Keep Records for Future Reference
Store copies of tax returns, receipts, and proofs for at least 5–7 years to facilitate audits, corrections, or disputes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Filing past deadlines or missing quarterly installments
- Underreporting income or overstating deductions
- Ignoring documentation requirements
- Failing to pay taxes owed on time
- Not staying updated on changing tax laws
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your filing is accurate, legal, and stress-free.
Tips for Filing Taxes Correctly
- Use tax software or online portals for calculations and submissions
- Consult a tax professional if your financial situation is complex
- Keep updated with changes in tax regulations and new deductions
- Start the tax filing process early to avoid last-minute errors
- Maintain organized records throughout the year
Conclusion
Understanding tax filing rules explained is vital for individuals and businesses to remain compliant, minimize tax liability, and make informed financial decisions. Accurate reporting, timely payments, and proper documentation ensure a smooth filing process, reduce penalties, and allow you to maximize deductions and exemptions.
Filing taxes correctly is more than a legal requirement—it is a critical step in financial planning, saving money, and securing your financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Tax Filing Rules Explained
1. What are tax filing rules?
Tax filing rules are the regulations and procedures set by tax authorities that define how, when, and what taxes must be reported and paid.
2. Who must follow tax filing rules?
All individuals earning taxable income, freelancers, self-employed professionals, and businesses must comply with applicable tax filing rules.
3. Why is it important to follow tax filing rules?
Following rules ensures legal compliance, avoids penalties and interest, maximizes deductions, and reduces the risk of audits.
4. What documents are required to file taxes correctly?
Common documents include salary slips, bank statements, investment proofs, home loan statements, insurance receipts, and business records.
5. How do I determine which income is taxable?
All income sources—salary, business or freelance income, rental income, investment gains, and bonuses—must be reported according to tax laws.