Tax planning for individuals is one of the smartest financial practices you can adopt to manage your income efficiently and legally reduce your tax burden. Instead of waiting until the last moment to file returns, proactive tax planning helps you make informed decisions throughout the year, ensuring better savings, compliance with tax laws, and long-term financial stability.
In today’s evolving tax environment, understanding how tax planning works is no longer optional—it is essential for salaried employees, freelancers, business owners, and investors alike.
What Is Tax Planning for Individuals?

Tax planning for individuals refers to the strategic analysis of a person’s financial situation with the objective of minimizing tax liability while remaining fully compliant with the law. It involves evaluating income sources, investments, expenses, and available deductions or exemptions to ensure that you pay only what is legally required.
Effective tax planning is not about avoiding taxes; it is about optimizing your finances using lawful provisions offered by tax authorities.
Why Tax Planning Is Important
Tax planning offers multiple benefits beyond tax savings. Here’s why it plays a crucial role in personal finance:
- Reduces tax liability legally
- Improves cash flow and savings
- Encourages disciplined investments
- Helps achieve long-term financial goals
- Prevents last-minute tax stress and penalties
Without proper tax planning for individuals, many people end up paying more taxes than necessary simply due to lack of awareness.
Types of Tax Planning for Individuals
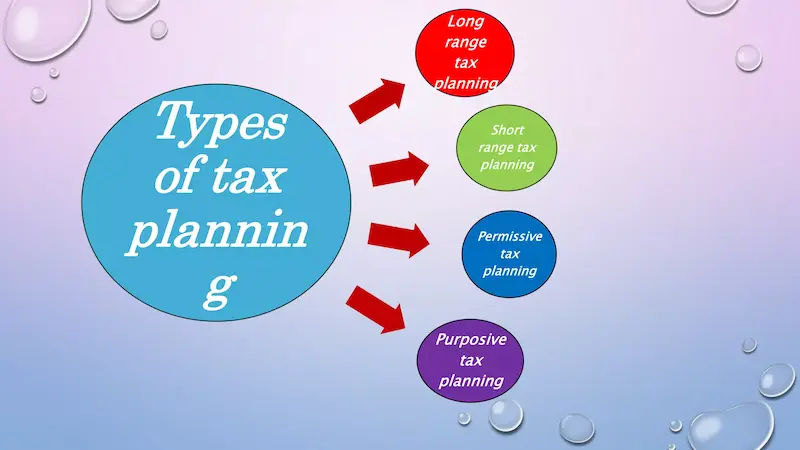
Understanding different types of tax planning helps you choose the right approach based on your financial goals.
1. Short-Term Tax Planning
This focuses on minimizing taxes at the end of the financial year using last-minute investments or deductions. While helpful, it is less effective than long-term planning.
2. Long-Term Tax Planning
Long-term tax planning involves investments and strategies implemented early in the financial year or over several years, such as retirement plans and long-term savings instruments.
3. Permissive Tax Planning
This type uses deductions, exemptions, rebates, and allowances explicitly permitted by tax laws.
4. Purposive Tax Planning
Purposive tax planning aligns financial decisions—like asset purchases or business structuring—with tax-saving objectives.
Key Tax-Saving Instruments and Strategies
Successful tax planning for individuals relies on understanding available tools and using them wisely.
1. Retirement Contributions
Contributing to pension funds, provident funds, or retirement savings schemes not only secures your future but also provides significant tax deductions.
2. Health Insurance Premiums
Premiums paid for health insurance often qualify for tax benefits, while also offering financial protection against medical emergencies.
3. Education and Housing Benefits
Education expenses, student loan interest, and home loan interest or principal repayments may be eligible for deductions, depending on local tax laws.
4. Investment-Based Tax Savings
Investments in government-approved savings schemes, mutual funds, or bonds can reduce taxable income while generating long-term returns.
5. Income Splitting and Family Planning
In certain jurisdictions, distributing income among family members through legal means can help lower the overall tax burden.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Tax Planning
Even with good intentions, individuals often make errors that limit the effectiveness of tax planning.
- Waiting until the last month of the financial year
- Investing only for tax benefits without considering returns
- Ignoring proper documentation
- Not reviewing tax plans annually
- Misunderstanding eligibility for deductions and exemptions
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your tax planning for individuals remains efficient and compliant.
You may also like to read this:
Best Tax Saving Ideas: Legal Ways to Reduce Taxes
Personal Tax Planning Guide: Save Taxes & Maximize Savings
Tax Planning for Small Businesses: Save Taxes Legally
Income Tax Planning Tips: Save Taxes Legally
Tax Planning for Salaried Individuals vs. Self-Employed
Salaried Individuals
They typically benefit from standard deductions, employer-provided benefits, retirement contributions, and insurance-related tax relief.
Self-Employed and Freelancers
They can claim deductions for business expenses, depreciation, office rent, utilities, and professional development costs—making tax planning even more critical.
Role of a Tax Professional
While basic tax planning can be done independently, consulting a qualified tax advisor can add immense value. Professionals help interpret complex laws, identify overlooked deductions, and design personalized tax-saving strategies based on your income and life stage.
How to Start Tax Planning Today
To get started with tax planning for individuals, follow these simple steps:
- Analyze your income sources
- Track expenses and savings
- Understand applicable tax slabs and laws
- Identify eligible deductions and exemptions
- Invest early and review periodically
Consistency is the key to effective tax planning.
Conclusion
Tax planning for individuals is not just about saving money—it’s about taking control of your financial future. With proper planning, awareness, and timely action, you can reduce tax stress, increase savings, and achieve your long-term goals with confidence.
Whether you are just starting your career or planning retirement, smart tax planning ensures that your hard-earned money works harder for you—today and in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Tax Planning for Individuals
1. What is tax planning for individuals?
Tax planning for individuals is the process of organizing income, expenses, and investments in a legal way to reduce tax liability while complying with tax laws. It helps individuals save money and manage finances more effectively.
2. Who should do tax planning?
Tax planning is important for everyone, including salaried employees, freelancers, business owners, and investors. Anyone earning taxable income can benefit from proper tax planning.
3. When is the best time to start tax planning?
The best time to start tax planning for individuals is at the beginning of the financial year. Early planning provides more options, better investment choices, and avoids last-minute stress.
4. Is tax planning legal?
Yes, tax planning for individuals is completely legal when done within the framework of tax laws. It uses approved deductions, exemptions, and allowances to reduce tax liability.
5. What is the difference between tax planning and tax evasion?
Tax planning is a lawful method of minimizing taxes using legal provisions. Tax evasion is illegal and involves hiding income or providing false information to avoid paying taxes.